Telemetry
Heterogeneous Combination of Navigation-Based Technology and Telemetry

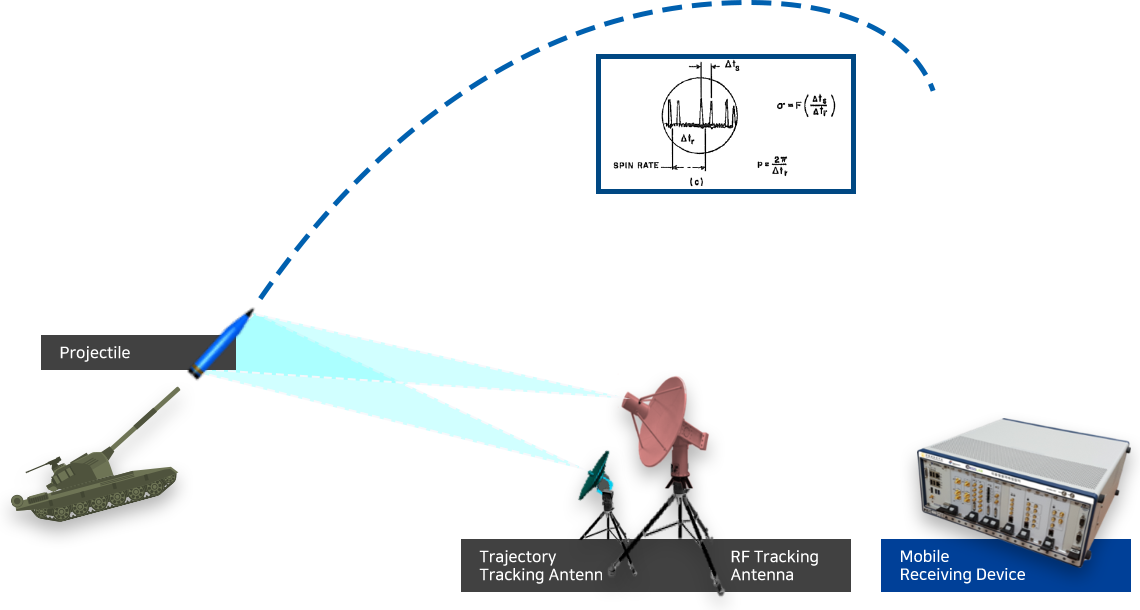
It withstands the high impact of artillery firing in the form of a standard fuse and measures signals (rotation & attitude) using the Yawsonde sensor, which uses the sun light sensor.
After measuring and sampling the signal, it converts into a digital signal and an RF signal and transmits the signal to the receiver on the ground using a telemetry that serves to transmit the signal to the antenna.
After measuring and sampling the signal, it converts into a digital signal and an RF signal and transmits the signal to the receiver on the ground using a telemetry that serves to transmit the signal to the antenna.
Ballistic Trajectory Data Transmitter
Ballistic Data
Transmitter
Yawsonde
Sensor
Telemetry
Features
- After Acquiring the Information of the Projectile, Transmitting it to the Ground via Telemetry
- Information from Projectile: Yawsonde Sensor, Magnetic Sensor, Gyro etc.
- Small Ballistic Trajectory Data Transmitter for High Rotation/High Impact
- Flight Trajectory Data Analysis & Database Establishment
Telemetry
Innovative Combination of GNSS Navigation Technology and Telemetry

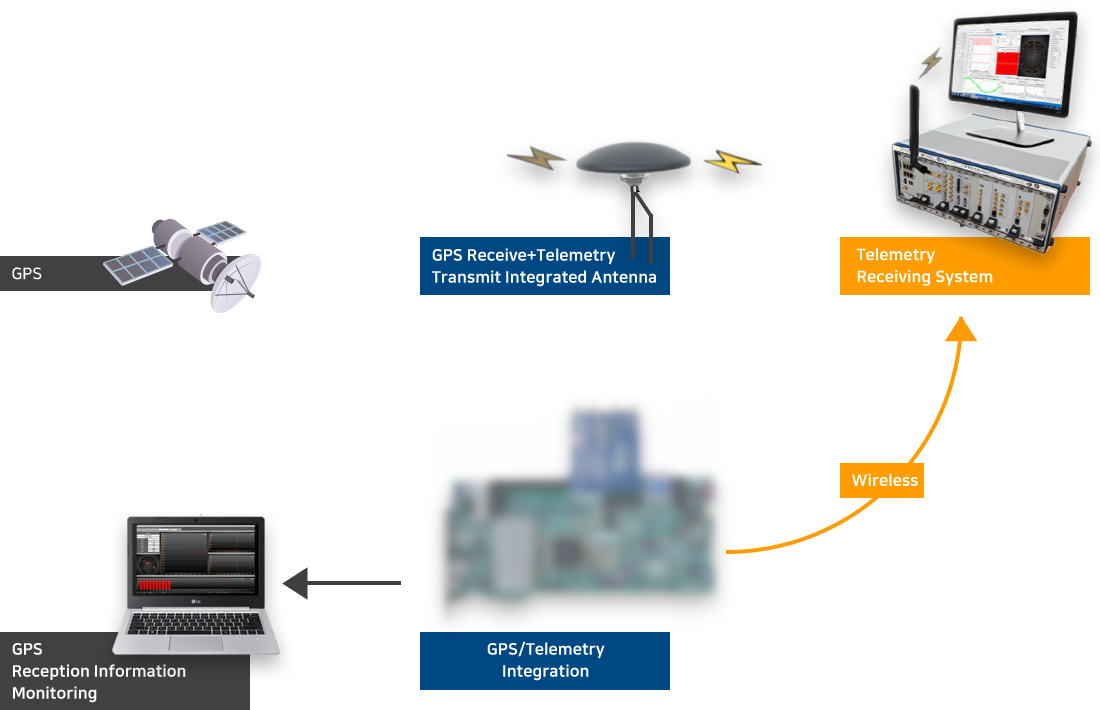
It combines GPS receiver and telemetry transmitter into one module, which is essential for guided weapon systems that require trajectory or track information of fast-flying/moving objects over long distances.
Not only have they solved the interference between GPS and telemetry RF, but they can also be miniaturized, reduced in cost, and integrated in unit operation.
There is no similar solution in the global market, and it can be embedded in the weapons system at all times to be useful for training and maintenance during system operation.
Not only have they solved the interference between GPS and telemetry RF, but they can also be miniaturized, reduced in cost, and integrated in unit operation.
There is no similar solution in the global market, and it can be embedded in the weapons system at all times to be useful for training and maintenance during system operation.
Features
- RF Interference Resolving: GPS Receiving Antenna and Telemetry Transmitting Antenna
- Small and Lightweight Implementations Applicable to Various Systems
- Low Cost Module Offers Price Competitiveness (for Mass Production Tests, Training Tests and Battlefield Applications)
Specifications
Frequency Band
- GPS L1 C/A, GLONASS L1 C/A, S-Band (2,200 ~ 2,390MHz)
- 24 Channels
- 1Mbps
- GPS Data and System status information
- 1W (can be changed according to customer request)
- GPS, GLONASS 0dBic or better / TLM 0dBi (@ 2.2GHz) or better
- 40dB or more
- Negotiable according to customer requirements
Telemetry
Universal Mobile Telemetry Device for Acquisition of Flight Information of Projectiles

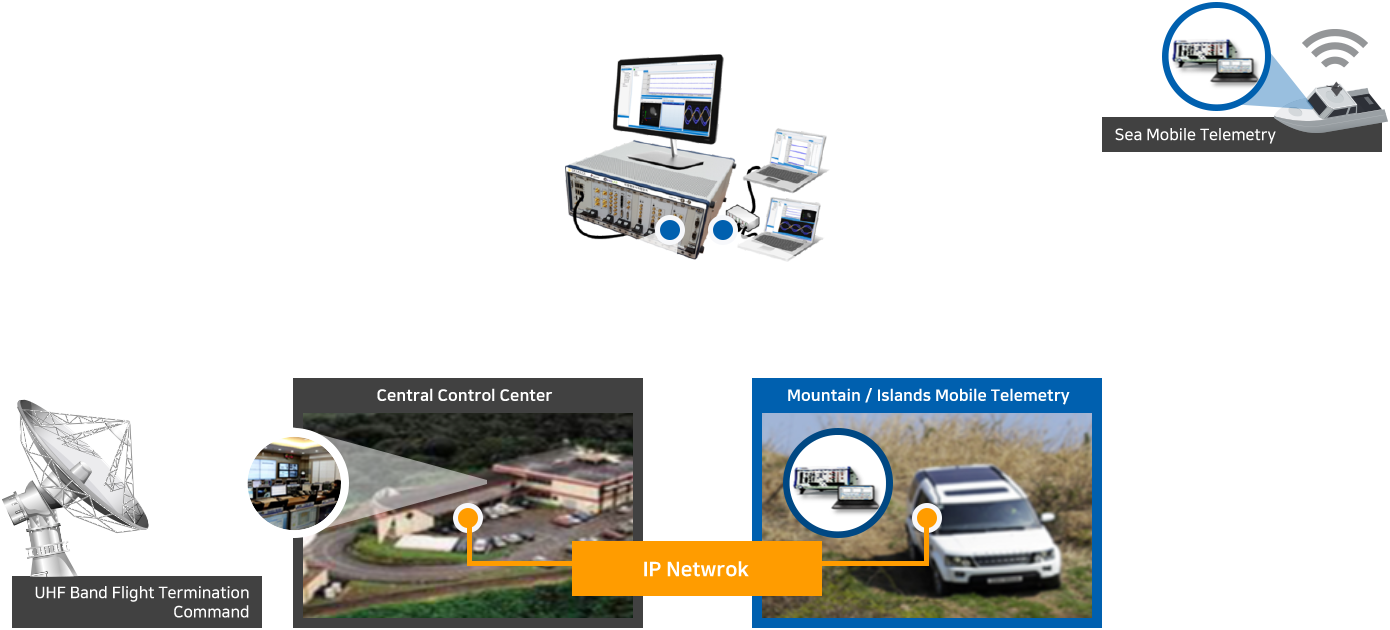
The telemetry system acquires flight and status information of projectiles and displays them in real time in a form that can be analyzed by the user, and simultaneously stores them in internal storage.
The stored data has the function to transmit and share it to other remote sites, and each function is implemented in a modular form and mounted on the Rack, making it easy to carry and move.
The stored data has the function to transmit and share it to other remote sites, and each function is implemented in a modular form and mounted on the Rack, making it easy to carry and move.
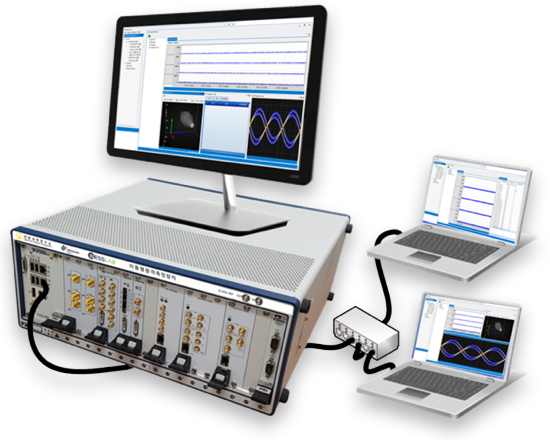

Size
- 19”4U rack-mount
- max. 32bit
- 30ns rms
Features
- Acquisition and Control Internal Information and Status of Measurement Targets such as Aircraft, Drones, and Guided Weapons
- Modularization of System Components through Functional Modularity
- Real Time Data Processing with User Processing Algorithm and Storing
- Real Time PCM Signal Transmission via Ethernet
- Providing Various Display Charts
Telemetry
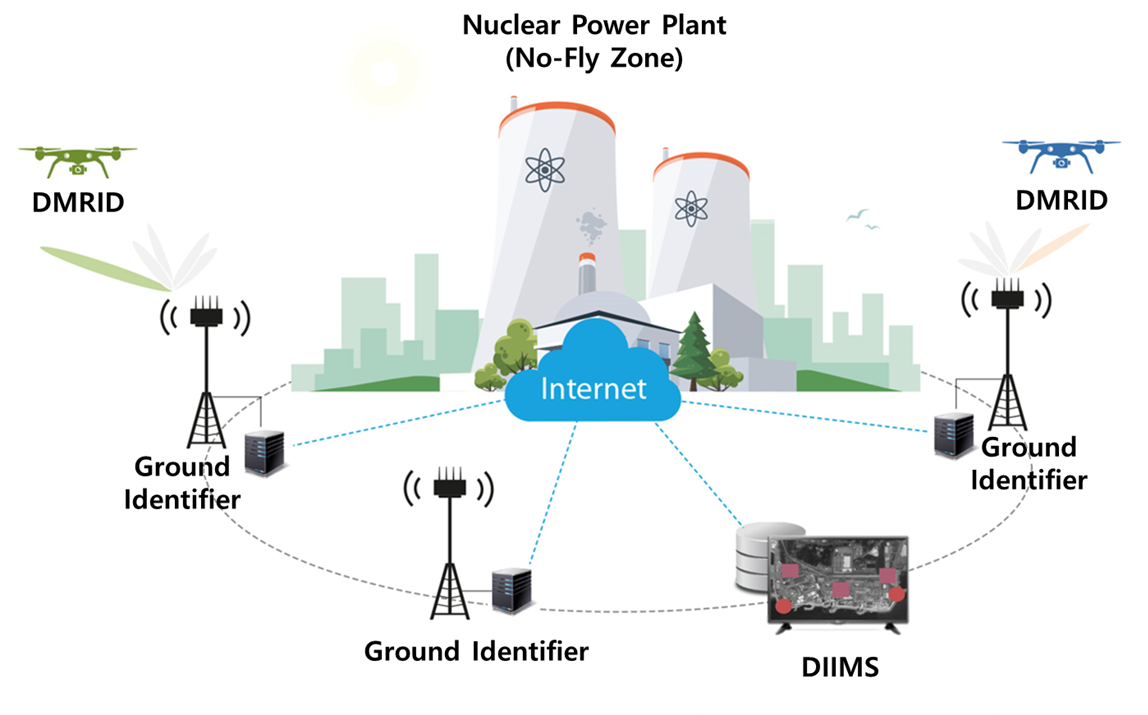
Drone Remote Identification Device

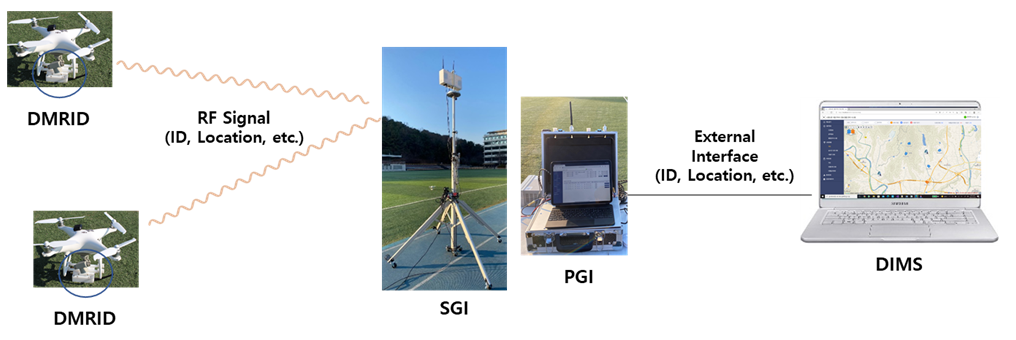
The DRID contains a drone mounted remote identification device(DMRID), a stationary ground identifier(SGI), and a portable ground identifier(PGI). The DMRID transmits the drone identification information with RF signals.
The SGI and the PGI obtain the drone identification information from the received RF signals. Note that the information can be managed by a drone identification information management system(DIIMS).
The DMRID, the SGI, and the PGI can support two transmission schemes; direct sequence spread spectrum and Wi-Fi.
Features
- Comply with the FAA and the EASA remote ID regulations
- Improve drone identification distance two times than the conventional devices
- Provide the drone identification information through map-based website
DMRID
Frequency
- 2.4GHz, 5.8GHz
- < 20dBm
- 1 Tx
- GPS, GLONASS
- Spred Spectrum, Wi-Fi(Beacon)
- ID, Drone Location, Drone Altitude
- Speed, Direction, Takeoff Location
- Takeoff Altitude, Timestamp
- Emergency Status
- < 1sec
- -
SGI
Frequency
- 2.4GHz, 5.8GHz
- -
- 2 Rx
- GPS, GLONASS
- Spred Spectrum, Wi-Fi
- -
- -
- Ethernet, Wi-Fi
PGI
Frequency
- 2.4GHz, 5.8GHz
- -
- 2 Rx
- GPS, GLONASS
- Spred Spectrum, Wi-Fi
- -
- -
- Ethernet, Wi-Fi
Applications
Anti-drone service to protect important national facilities from illegal dronesFollow-up service such as responsibility identification and insurance processing in the event of safety accidentService to prevent invasion of privacy using illegal drones